Phase Inversion Detection: Difference between revisions
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
==Phase Inversion using PCM== | ==Phase Inversion using PCM== | ||
[[File:PCMPalette.PNG|thumb|Standard PCM Palette.]] | |||
The PCM method of determining Phase Inversion uses a combination of Peak-to-Peak amplitude and a custom palette. Options allow the user to adjust the algorithm to use Peak Amplitude, order of peaks, or both. | The PCM method of determining Phase Inversion uses a combination of Peak-to-Peak amplitude and a custom palette. Options allow the user to adjust the algorithm to use Peak Amplitude, order of peaks, or both. | ||
Revision as of 12:29, 28 May 2025
Multiple methods can be used to determine if a Phase Inversion occurs within a sample. Phase inversion can indicate a problem such as delamination within a part.
Phase Inversion with RTG Gates
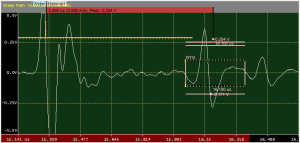
An RTG Gate runs an algorithm to determine if a Phase Inversion occurs. In summary, the gate checks that the following conditions are met:
- Absolute Peak Amplitude exceeds the Consider Threshold
- No Negative Peak is found or a negative peak occurs after the Positive Peak
- The Positive Peak crosses one or more Relative Threshold gates (the amplitude of which is determined by the absolute peak)
Note: RTG Gates are available in Hardware peak detection for 8xGTE A/D boards: for other devices, RTG Gates must be run with Software Peak Detection.
RTG Settings
An RTG Gate has the following settings:
- Start
- Length
- Standard Threshold, any signal under the threshold is ignored. This behaves the same as any Data gate threshold.
- Consider threshold, usually set above the standard threshold: only if the APA exceeds this value will a Phase Inversion check occur)
- Relative Thresholds, numbered 1-3, these are set at Percentages of the APA, not as absolute thresholds. Therefore, the "absolute" threshold of these gates will vary with the peak amplitude. There will be two positive and one negative relative thresholds.
Phase Inversion Algorithm
To run a Phase Inversion check, the algorithm proceeds as follows:
- did any signal exceed the standard Threshold? If not, stop.
- record the APA, PPA, NPA, THPP, THNP values in the gate.
- did the APA exceed the consider threshold? If not, stop.
- Phase Inversion Check:
- adjust the relative thresholds based on the APA, e.g. if the APA is at 80% FSH, and the negative relative threshold is set for -60%, the "working" relative threshold is 80 * -.6 = -48%
- does a signal cross the negative relative threshold before crossing the positive relative threshold? If so, stop.
- If there is no negative signal crossing the negative relative threshold or it occurs after the positive relative threshold, check the postive relative thresholds.
- Does the positive peak cross one or more of the positive relative thresholds? Then record as phased inverted, with the intensity being the maximum relative threshold crossed.
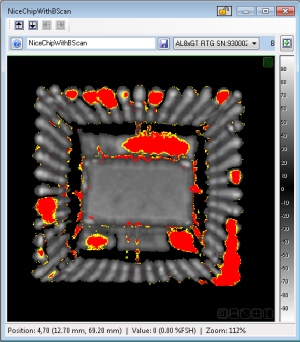
On the image, this will result in a map that shows normal Peak data if no Phase Inversion is detected, or colors representing the intensity of the Phase Inversion. By default, those colors are Red (High) and Yellow (Low).
Phase Inversion using PCM
The PCM method of determining Phase Inversion uses a combination of Peak-to-Peak amplitude and a custom palette. Options allow the user to adjust the algorithm to use Peak Amplitude, order of peaks, or both.
PCM can be used on any Data Gate.
PCM Settings
The data Gate has the following settings:
- Start
- Length
- standard Threshold, any signal under the threshold is ignored.
- Consider threshold, usually set above the standard threshold: only if the APA exceeds this value will a Phase Inversion check occur)
The PCM Palette