Collection Cycle: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "==The Basics== <p>Data collection requires four pieces of equipment: #an Analog-to-Digital Converter (A/D) board, #a Pulser/Receiver (P/R), #an ultrasonic transducer, #a standard desktop or laptop computer to display the resulting information.</p> <p>In a data collection, the P/R is triggered (often by a signal from the A/D board) which sends a burst of electricity to the ultrasonic transducer. This excites the transducer, which generates a burst of ultrasound. The...") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==The Basics== | ==The Basics== | ||
<p>Data collection requires four pieces of equipment: | <p>Data collection requires four pieces of equipment: | ||
#an Analog-to-Digital Converter (A/D) board, | #an Analog-to-Digital Converter ([[Glossary of Terms#A|A/D]]) board, | ||
#a Pulser/Receiver (P/R), | #a Pulser/Receiver ([[Glossary of Terms#P|P/R]]), | ||
#an ultrasonic transducer, | #an ultrasonic [[Glossary of Terms#T|transducer]], | ||
#a standard desktop or laptop computer to display the resulting information.</p> | #a standard desktop or laptop computer to display the resulting information.</p> | ||
Latest revision as of 11:49, 13 June 2025
The Basics
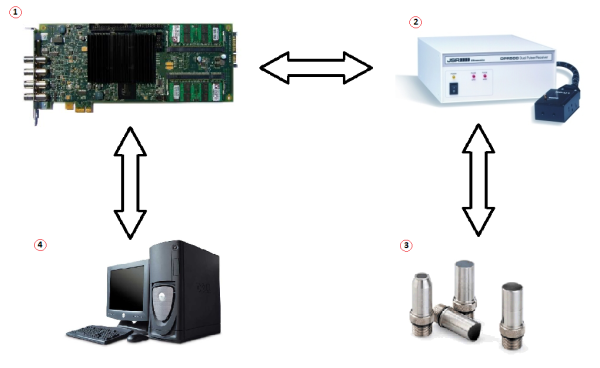
Data collection requires four pieces of equipment:
- an Analog-to-Digital Converter (A/D) board,
- a Pulser/Receiver (P/R),
- an ultrasonic transducer,
- a standard desktop or laptop computer to display the resulting information.
In a data collection, the P/R is triggered (often by a signal from the A/D board) which sends a burst of electricity to the ultrasonic transducer. This excites the transducer, which generates a burst of ultrasound. The returning ultrasound is sent back to the P/R, which sends the resulting waveform to the A/D board. The A/D board turns the waveform into digital information, which is processed into Peak Amplitude and Time of Flight results.
By continuously triggering the P/R while moving the transducer along an axis, we can generate results along a scan line. By stepping along a second axis after each scan line, a raster image of data is generated.
The trigger of the P/R is synchronized to the start of collection on the A/D board, so that the waveforms are always generated at the same point in time. In practice, this usually means that the A/D board itself sends the trigger to the P/R.
See Also: Triggering