Cluster Analysis
Cluster Analysis allows for particle recognition in target sample images. Tolerances and margin critera are user configurable prior to detection of clusters. The analysis returns a table containing bounding rectangle information, along with total area and data point counts. The clusters themselves can be highlighted on the image. The cluster results can be exported to CSV, XML or Text files for further analysis.
Configuring Cluster Analysis
To configure Cluster Analysis, select an image window and then click on the "Cluster Manager" icon. This will cause the Cluster Setup window to appear. Manual Cluster Analysis will operate on a single feature at a time: the selected feature is shown in the title bar of the Cluster Setup window.
As of this writing, cluster analysis can only be performed on Peak Amplitude images.
The Cluster setup window has four tabs for specific inputs (the "Depth" tab, as of this writing, is reserved for future changes)
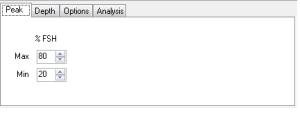
Peak Tab
The "Peak" tab defines the range of data for which cluster data will be marked. This is specified in terms of %FSH. On a grayscale image, if defects are bright regions, the min and max should be set for high % (e.g. 80-100%). If defects are darker regions, a low range should be specified (e.g. 0-30%). Note that these ranges only go from 0-100%: negative peak results are rectified in the algorithm, e.g. a peak of -10% FSH is treated as 10% FSH. Detected defect regions are called clusters.
Depth Tab
Reserved for future changes.
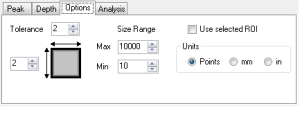
Options Tab
The "Options" tab specified several settings that affect the cluster search results:
- Tolerance
- this specifies how close two clusters have to be to be considered part of the same defect. A tolerance of 0 means that data points must be touching horizontally before being considered part of the same cluster. Increasing tolerance will allow clusters that are separated by a gap to be considered part of the same result. Tolerance can be specified on both the vertical and horizontal axes. This will affect the overall % of cluster data found and the bounding dimensions for clusters.
- Size Range
- this specifies the minimum and maximum sizes of detectable clusters, in terms of data point counts (if using pixels) or square units (if using mm or inches). A cluster that falls outside this range will not be marked. The number of clusters that are outside the specified ranges will be listed above the cluster result table on the Analysis Tab.
- Units
- the units in which to specify the tolerance and range. By default, pixels (i.e. Data Points) are used. The user can also specify inches or mm.
- Use Selected ROI
- if one or more Shape annotations are present on the image (rectangle, polygon, etc) the cluster analysis will be restricted to the shape regions. Otherwise, cluster analysis will take place on the whole image.
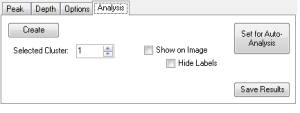
Analysis Tab
The Analysis tab is where the user starts Cluster Analysis.
- Create
- this button starts the analysis. When the analysis is finished, the table below the controls will list the cluster sizes, locations, and dimensions. The clusters will also be displayed on the image based on the following options.
- Create Using Image
- if checked, the cluster analysis will use the image bitmap data to detect clusters and not the raw results. Note: this option should be used by advanced operators only.
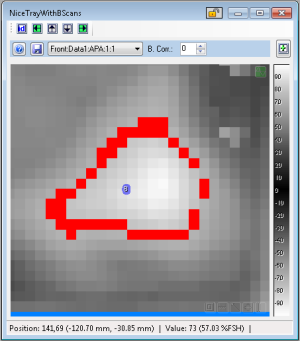
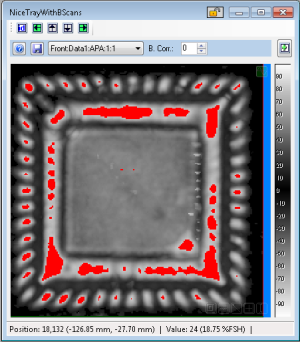
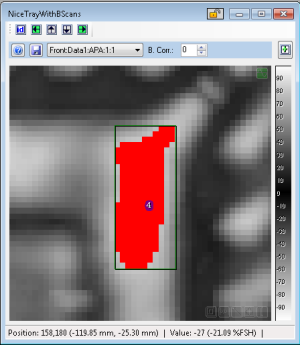
- Show On Image
- if checked, the cluster results will be displayed on the image data as red data points. This color can be changed in Configuration.
- Hide Labels
- if not checked, the displayed clusters will show the cluster index value assigned as a text annotation. This index is displayed at the center of the cluster (based on the Bounding Area). If not checked, these annotations will not be displayed.
- Selected Cluster
- Once clusters are created, the user can highlight a cluster by using the "Selected Cluster" spin control. This is the same as clicking on the cluster entry in the table of results.
- Set for Auto-Analysis
- This transfers the cluster configuration to the Auto-Analysis setup.
- Save Results
- This will open a dialog that allows the user to save the cluster results. Cluster Analysis results can be saved to Text, CSV, or XML files for external analysis.
Quick Setup
- Open the Cluster Analysis window.
- On the Peak tab, Select a %FSH range
- (Optional) On the Options tab, "use selected ROI" to restrict the cluster analysis to the area in a shape annotation (Area, Frame, or Polygon)
- On the Analysis Tab, Click on "Show On Image"
- (Optional) on the image, use the Select tool and/or click on the annotation you want to use
- On the Analysis Tab, Click "Create"
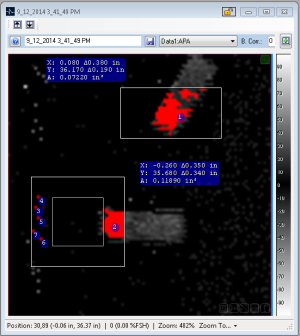
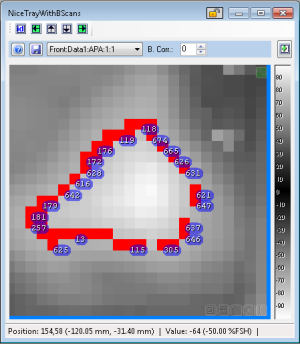
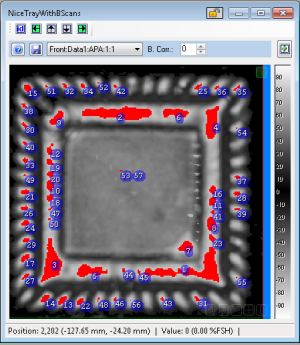
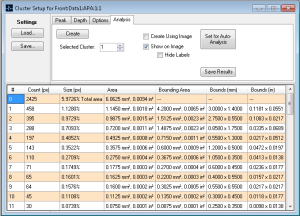
Cluster Results
The result of a cluster analysis consists of two pieces of data:
- A sortable grid on the Cluster Setup window showing the sizes, bounding rectangles, and data point counts of detected clusters (by default, they are put in order from largest to smallest).
- An overlay on the visible feature showing the exact shape and location of any clusters.
The grid shows the following Results:
- Index
- This is the assigned index of the cluster. The "0" index shows the overall percentage and size of the results, as compared to the whole image (or the selected ROI). The index will also be displayed on the image if the Hide Labels option is unchecked.
- Count(px)
- This is the total number of image data points that make up the cluster.
- Size(px)
- This is the percentage of the overall area that this cluster covers; e.g. if a cluster covers 50 out of 200 data points, it has a coverage of 25%.
- Area
- This is the area covered by the cluster in physical units (mm2 and inches2).
- Bounding Area
- This is the area covered by the bounding rectangle of the cluster in physical units (mm2 and inches2). The bounding area of a cluster will be displayed on the image when the "Bounding Area" column of is selected with the left mouse button.
- Bounds (mm and inches)
- This shows the dimensions of the bounding rectangle of the cluster in physical units.
Clicking or moving the focus on the grid will highlight the cluster on the original image (if the "Update" checkbox is set). The selected cluster's bounding box will be displayed if the user is selecting the "Bounding Area" column.
If any clusters are found that are above or below the minimum size requirements, this will be indicated on the Analysis tab.
Loading and Saving Cluster Setups
Cluster setups (including threshold, tolerance and min/max size information) can be saved to disk using the "Save..." button at the upper right of the Cluster Setup window. These settings are saved in an XML file with the extension ".cluster.xml".
Cluster setups can be reloaded at any time using the "Load..." command, which will open a file dialog that allows the user to select from the available cluster configuration files.
Cluster Analysis and Auto-Analysis
See Also:Auto-Analysis
Cluster analysis is a major part of automatic analysis checks: a setup similar to the cluster analysis window is used to determine cluster setups on one or more regions of interest. Cluster setups that are saved to disk can be loaded into Auto Analysis as needed using the "Set for Auto-Analysis" button on the Cluster Setup window.