Gate Features
See Also: Gates
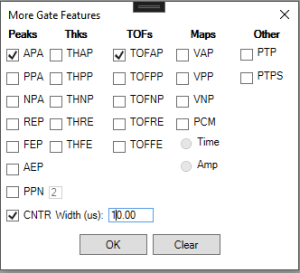
each Gate Region can collect one or more Gate Features. A Gate Feature is a type of information collected from the Gate Region.
Peak Amplitude
Peak Amplitude is a value that represents the largest peak within a data gate. Amplitude is collected in terms of %Full Screen Height (%FSH) or Voltage. A value of 0 is considered "Peak Not Found".
Commonly, the Absolute Peak Amplitude is stored in the collection. The value can be further separated into the Positive Peak or Negative Peak.
Peak Amplitude is one of the main features of a Data Gate.
When saving Peak Amplitude data to a file, the sign of the amplitude data is preserved.
For A/D boards that collect 8-bit data, the Peak Amplitude image is stored as signed bytes, ranging from -128 to 127. For 12-bit and higher boards, the image is stored as signed words ranging from -32768 to 32767.
Peak-to-Peak
Amplitude data can also be stored as the difference between the positive and negative peaks. When saving Peak-to-Peak data to a file, the data is unsigned.
For A/D boards that collect 8-bit data, the Peak-to-Peak image is stored as unsigned bytes, ranging from 0 to 255, For 12-bit and higher boards, the image is stored as unsigned words ranging from 0 to 65535.
Signed Peak-to-Peak
When using RTG gates when inverting the signal on the Digital Oscilloscope, a signed Peak-to-Peak image will be generated instead of the normal RTG map. The Signed peak-to-peak retains the sign of the larger of the two peaks.
First Peak
The amplitude of the First peak (after the data gate threshold is crossed) can also be collected. In this case, the peak data is not necessarily the largest peak in the signal. Either the Rising Edge Peak, the Falling Edge Peak, or the Absolute Edge Peak (the Earlier of the Rising or Falling Edge Peak) can be collected.
Data ranges and storage are exactly the same as with a conventional Peak Amplitude image.
Time of Flight
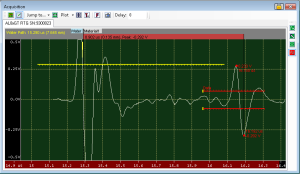
Time of Flight (TOF) is the amount of time it takes to reach the desired feature in a gate. The TOF to a feature is calculated in units of time, generally microseconds. TOF measurements start from time zero (e.g. the "Main Bang" on the Digital Oscilloscope) and end at the feature in the gate.
Follower Gates collect a TOF value by default. For a Front Surface follower gate, the TOF is also called the Water path.
Another common TOF measurement is the Time to the Absolute Peak. This generates a TOF map that shows the relative positions in time of the peak values. On a grayscale image, features that are further in time (i.e. deeper into the part) will be dark, whereas features that are closer in time will appear brighter.
TOF images are stored in 32-bit dwords, where a value of 231 is considered to be "TOF not found", and a value of 0 is considered to be "Parent not found" (for example, if the Data Gate is tracking a Follower Gate and the follower is not crossed). The values are in terms of A/D samples, thus a change in sampling rate will result in a different stored value for the same amount of time.
Thickness
Thickness is the relative TOF from features in one gate to another gate. By default, this is used to determine the time from the crossing point of a Follower Gate to the Peak of a Data Gate. By using Advanced follower settings, the user can generate a thickness map that is between two peaks, or two rising/falling edges, depending on the gate settings.
Storage and values of Thickness images are identical to that of a TOF collection.
Rising and Falling Edges
The TOF to the Rising and/or Falling Edge of a gate can also be collected. Storage and values are identical to a regular TOF collection.
RTG Map
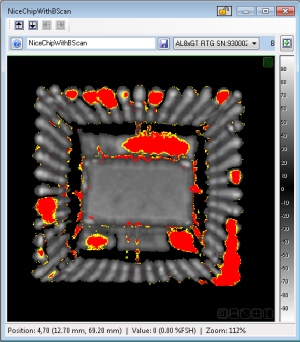
An RTG Map shows the points on an image where Phase Inversion was detected. RTG maps are generated by Relative Threshold Gates only.
An RTG map has only three possible values: "High", "Low", and "None". In ODIS, the "High" value is represented by red, and the "Low" value is represented by yellow.
An RTG map is stored in packed 2-bit bytes, four results to a byte.
In general, an RTG map is superimposed on another image type (usually the Absolute Peak Amplitude) to show the relative location of the phase inversion.
Void Map
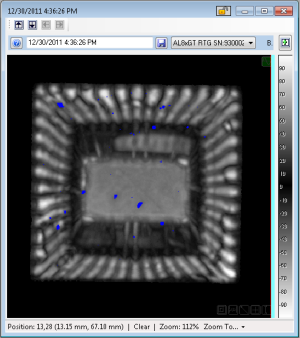
a Void Map shows points on an image where data crossed the Void Detection thresholds of a Void Gate. Void maps are generated by Data Gates.
A Void map has only two possible values: "High", and "None". In ODIS, the "High" value is represented by blue.
A Void map is stored in packed 2-bit bytes, four results to a byte.
In general, a void map is superimposed on another image type (usually the Absolute Peak Amplitude) to show the relative location of the phase inversion.
Frequency Domain Features
Frequency Domain features are collected by the FFT Gate only. The waveform covered by this region generates an FFT from which features are extracted.
Peak Frequency
The peak frequency is the index of the frequency with the greatest amplitude in the Magnitude Spectrum.
Center Frequency
The Center frequency is the midpoint of the frequencies between the 6dB down and 6dB up value. Will differ slightly from the Peak Frequency if the slope of the curve around the Peak Frequency differs on the down side than the up side.
3dB/6dB/Up/Down
The frequency(ies) at which the amplitude from the peak is 3/6 dB down (towards lower frequencies) or up (towards Higher Frequencies).
Frequency Gate Features
Some Features can be collected using the Frequency Gates on the Magnitude Spectrum