Digital Oscilloscope
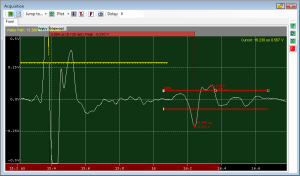
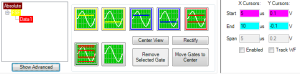
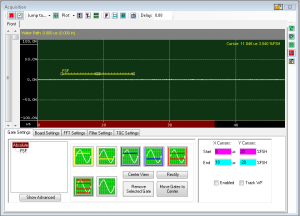
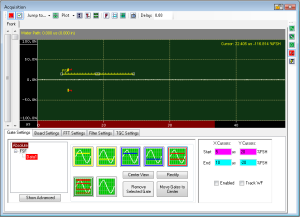
The Digital Oscilloscope is the heart of ODIS. From this window, the user can manipulate the waveform returned from an A/D board and set up Gates to collect features.
Overview
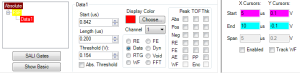
The Scope consists of a waveform display region and controls for manipulating the results. There may be one or more display regions, depending on the number of A/D boards in the system. Each board's result is shown in a separate tab.
parameters can be copied from one channel to another. First, right-click on a channel tab and select "Copy Settings" from the resulting menu. Then right-click on the destination channel and select "Past Settings". This will copy the A/D and Gate setups from the source channel to the destination channel.
Note: if the source and destination channels are different types of A/D boards, some settings may not be transferred.
Scales
The vertical scale of the scope measures the intensity of the returning signal. The scale can be set in Volts, %FSH, or dB. To change the scale, click at the top left corner of the Scope window, at the topmost vertical units entry.
The Horizontal scale measures the time at which the signal is located. It can be displayed in either microseconds (us) or mm/inches, depending on your Configuration settings. To change the scale, click on the lower left corner of the scope, where the horizontal units are displayed.
Mouse Controls
There are a number of mouse modes available on the scope. In order to switch between them, the user moves the mouse over the scope window and right-clicks the mouse button to rotate through the controls. The controls available are listed below.
Zoom
The user can zoom in or out on the scope using two methods:
- use the Magnify Tool (
) To zoom in and out by left-clicking on the scope, holding the left button down, and move the mouse up and down. The point at which the user clicked will remain the "Center" of the zoom as the user moves the mouse.
- use the I-Beam Tool (I) to select a region of the scope on which to zoom. To make the selection, left-click and old the mouse on the scope, drag the mouse over the desired zoom selection, and release the mouse when done.
Pan
The user can pan the scope back and forth to see different positions in time. The pan control is the hand icon (). To pan the scope, left-click on the scope with the hand tool and hold the left mouse button down. Move the mouse left and right to pan the scope.
Gates
A user can click and drag on gate to move or resize them using the mouse. The Gate selection mode is the Arrow icon (). Gates have grab points at the left, right, and middle of the gate. Usually the leftmost point will move the gate, the middle point will change the gate threshold, and the rightmost point will change the gate length. Other points may be available depending on the gate type.
See Also: Gates and Regions
Toolbars
Controls
A number of controls can be made visible by pressing on the Controls button at the top left of the scope form (). These controls are subdivided into tabs based on the type of settings being manipulated.
Gate Settings
The Digital Oscillscope has controls for setting up you Gate Tree. There is a Basic Mode (not to be confused with the ODIS Basic Mode and an Advanced Mode for finer control. In Both cases, gates are added to the Gate Tree (shown on the bottom left of the Gate Settings tab.
Basic Mode
The Basic mode consists of the Gate Tree and a set of buttons. To add a gate, press on the specified button. The gate will become a child of whatever gate is selected in the Gate Tree window.
Advanced Mode
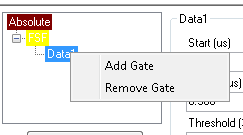
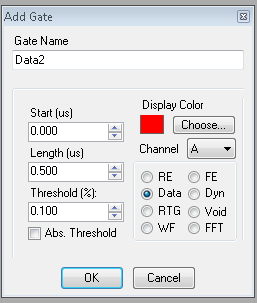
By clicking on the "Show Advanced" button, the user will see the Advanced gate settings. This allows for more gate options and better control over gate positioning. To add a gate, right-click on the Gate Tree and select "Add Gate". A dialog box will appear letting the user specify the gate type and settings.
The gate will become the child of whichever gate was originally clicked.
|
File:SALIGateDialog.PNG Dialog when adding a SALI Gate. |
For more information on the gate types, see Gates and Regions.
Board Settings
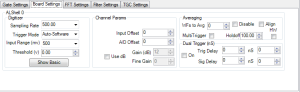
The Board Settings tab is used to control A/D board settings. Each channel has independent settings.
Note: exact board settings will vary among board types. Consult your board manual for details.
Digitizer Settings
- Sampling Rate
- The frequency at which the A/D board will sample the analog waveform data, in Megahertz (MHz). Available frequencies depends on the type of A/D board and OKOS_Controls_Config.xml options.
- Trigger Mode
- the method used to tell the A/D board to start collecting data.
See Also: Triggering
- Input Range
- the voltage range of the signal, in Millivolts (mV). The Y-scale of the Scope will use this range.
- Threshold
- Sets the voltage threshold for BNC and Threshold triggering, in Volts (v).
Status Indicators
- Encoder Position
- shows the current state of the encoder count on the A/D board.
- Temperature
- shows the current temperature of the A/D board. Consult your A/D manual for safe operating ranges.
Advanced Settings
- Input Offset
- A/D Offset
Averaging
Averaging allows the user to combine multiple waveforms in order to smooth out noise issues.
See Also: Waveform Averaging
- WFs to Average
- The number of waveforms to average together.
- Multitrigger
- whether or not to use Multitrigger mode when performing averaging.
- Holdoff
- the amount of delay (in microseconds) between Multitriggers.
- Align
- whether or not to attempt to align the collected waveforms to the Front Surface Follower crossing before averaging.
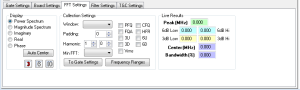
FFT Settings
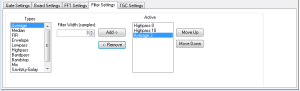
Filter Settings
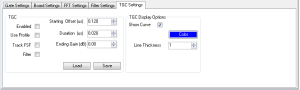
TGC Settings
The TGC Settings tab is where Time/Gain Corrections are made to the ultrasonic waveform. This lets the user compensate for signal loss as the sound travels deeper into the material of the part.
See Also: Time/Gain Correction (TGC)
Diagnostics
If Diagnostics are enabled, a few extra features are present.