ODIS Raw File Format
ODIS Raw File Format (ORFF)
ODIS raw data files are stored in a binary format, with XML files used to describe the image dimensions
and bit depth. Each feature of each gate is stored in a separate file. All the files of a particular scan are
called a Collection, and are stored in a directory with the same name as the Collection. Sub-Scans
(such as Sub B-Scans or Patch Scans) will be stored in a sub-directory.
Collection Directory Structure
Within a collections directory are one or more files.
EXTREMELY IMPORTANT: Do not move or rename these files manually. The file names are an important part of the collection structure, and it will be corrupted if they are changed.
Required Files
All ODIS collections require at least the following files:
- ScanParameters.set.xml
- ScanCollection.xml
- One or more binary files (.bin, .tiff, or .dcm)
- For each binary file, an XML description of the file using the same name (e.g. for binary file "X.bin", there must be a file "X.xml")
File Names
The scan name is a special format delineating the board, gate, feature and row/column (for tray scans) of the file. Names MUST be in the proper format or the file will be invalid.
The file name for any particular feature has the following format:
Raw_Brd<x>_Gate_Feature(_Row_Column)
- Brd<x>
- the board which collected this feature. x >= 0.
- Gate
- the name of the gate that was used to collect this feature.
- Feature
- a code representing the feature collected (Peak, TOF, etc.)
- Row and Column (optional)
- if this data is part of a Tray Scan, the row and column from which this data was collected is displayed here.
Examples:
Raw_Brd0_FSF_TOF = The Time of Flight information from the FSF gate on the first A/D board.
Raw_Brd1_Data1_APA_1_2 = The Absolute Peak Amplitude information from gate Data1 on the second A/D board, at Row 1, Column 2 of the tray scan.
Optional Files
ODIS collections may contain other files that store additional state information. These files are useful, but not required to read the raw data.
- For each binary file, a custom palette description using the same name (e.g., for binary file "X.bin", there would be a file "X.pal.xml"
- ScanAnnotations.xml
- ScanAnalysisSetup.analysis.xml
- ScanAnalysisResults.xml
- Info.xml
- AScan<X>.xml, where "X" is an identifier for the A-Scan (e.g. "AScan1.xml") (See Also: A-Scans)
- Sub-Directories containing Patch Scans and/or Sub B-Scans
Required Files Details
ScanCollection.xml
The ScanCollection.xml file contains the basic description of the Scan Collection. It lists all the image binary names and types, as well as some basic information about the collection. A typical file is shown below.
<Collection> <VERSION>ODIS 3.0</VERSION> <CollectionInformation> <name>NiceChipWithBScan</name> <comments>Built from ScanManager</comments> <starttime>6/3/2010 1:05:39 PM</starttime> <endtime>6/3/2010 1:14:31 PM</endtime> </CollectionInformation> <Files> <file ScanType="Scan_TOF">Raw_Brd0_FSF_TOF</file> <file ScanType="Scan_8bit_Peak">Raw_Brd0_Data_APA</file> <file ScanType="Scan_TOF">Raw_Brd0_Data_TOFAP</file> <file ScanType="Scan_8bit_Peak">Raw_Brd0_Data_PPA</file> <file ScanType="Scan_TOF">Raw_Brd0_Data_TOFPP</file> <file ScanType="Scan_8bit_Peak">Raw_Brd0_Data_NPA</file> <file ScanType="Scan_TOF">Raw_Brd0_Data_TOFNP</file> <file ScanType="Scan_TOF">Raw_Brd0_Data_THAP</file> <file ScanType="Scan_TOF">Raw_Brd0_Data_THNP</file> <file ScanType="Scan_TOF">Raw_Brd0_Data_THPP</file> <file ScanType="Scan_8bit_Peak">Raw_Brd0_RTG_APA</file> <file ScanType="Scan_RTG_Map">Raw_Brd0_RTG_DLM</file> <file ScanType="Scan_Waveform">Raw_Brd0_BScan1_WF</file> </Files> </Collection>
- Collection
- the root tag of the XML file.
- VERSION
- the version of the Collection XML file (this is *not* the same as the version of ODIS that generated the file).
- CollectionInformation
- the root tag containing basic information about the collection. Sub-tags include:
- name
- the name of the Collection ( should match the name of the directory in which the collection data is found).
- comments
- a ODIS-generated comment about the collection.
- starttime
- the time at which the collection was started.
- endtime
- the time at which the collection was ended.
- Files
- the root tag of the files description.
- file
- file tag contains the base name of the associated binary file. Each file tag has a ScanType attribute. The size of a sample in bytes depends on the Scan Type.
Scan Types
The Scan Type determines the type and bit depth of the data, and also lets a person determine what physical unit the integer values represent.
- Scan_TOF
- signed 32-bit data representing the TOF results. Data is stored in little-endian mode (LSB first). Low values indicate TOFs closer to the surface (i.e. closer to "Zero"), larger values indicate TOFs deeper in the sample. Samples can be converted into time by dividing by the Sampling Rate used to collect the data. A value of 0 is considered “TOF parent not found”, i.e. if the gate from which this data was derived has a parent; a value of int.MaxValue (231-1) is considered to be “Invalid Data”, e.g. TOF data was not found for this gate because the threshold was not crossed. Data range will vary depending on the gate settings.
- Scan_8bit_Peak
- signed 8-bit data representing Peak results. A value of 0 is considered to be “Peak not found” because the threshold was not crossed. Data can range from -128 to 127.
- Scan_16bit_Peak
- signed 16-bit data representing Peak results. A value of 0 is considered to be “Peak not found” because the threshold was not crossed. Data can range from -32768 to 32767. Data is stored in little-endian mode (LSB first).
- Scan_8bit_Unsigned_Peak
- unsigned 8-bit data representing Peak-to-Peak results. Data can range from 0 to 255.
- Scan_16bit_Unsigned_Peak
- unsigned 16-bit data representing Peak-to-Peak results. Data can range from 0 to 65535. Data is stored in little-endian mode (LSB first).
- Scan_Waveform
- signed 8-bit data representing waveform results (B-Scans). Data ranges from -128 to 127.
- Scan_16bit_Waveform
- signed 16-bit data representing waveform data (B-Scans) Data ranges from -32768 to 32767. Data is stored in little-endian mode (LSB first).
- Scan_RTG_Map
- 2-bit data packed into bytes. Each byte contains 4 results. Data ranges from 0 to 3.
- Scan_Encoder_Map
- Signed 32-bit data containing scalar results. Range is from -231 to 231-1. Data is stored in little-endian mode (LSB first).
ScanParameters.set.xml
This is the file detailing the scan parameters that were in place when the file was created. This file has a format identical to the standard Parameter File that is saved in ODIS, and can be loaded like a parameter file. This is useful if an operator wants to restore the state of the system when the scan was created, but does not have a separate parameter file available.
See documentation on Parameter Files for details.
Binary Files
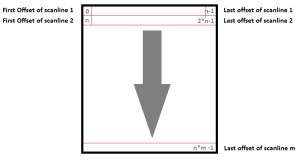
Each binary file is saved as raw data in scan line order. For example, In an 8-bit scan that is 10 pixels x 10 pixels, the first point of the first line would be at offset 0, the first point of the second scan line would be at file offset 10, etc.
Binary files have the extension “.bin” unless using the "Store as TIFF" or "Store as DICOM" options (see below).
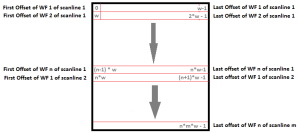
For B-Scans, the data is saved in waveform order. For example, in an 8-bit waveform that is 10x10x200 (where 200 is the number of samples in the waveform), the first waveform of the first scan line would be at offset 0, the second waveform would be at offset 200, etc. The first waveform of the *second* scan line would therefore be at 10x200 = 2000.
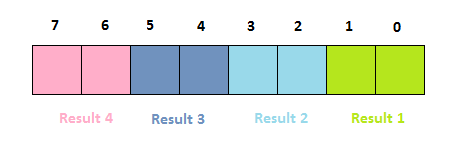
RTG maps pack four results to a byte, so RTG maps are 4x smaller than the equivalent 8-bit peak image. The map values are stored in LSB order within the byte:
Binary Files as TIFF
Optionally, a user may store the scan result data as a TIFF (Tagged Image File Format) image, which is readable in most standard imaging programs. In this case, the binary file is a standard TIFF and should be read as a normal image.
For 8-bit images (as described above), the TIFF image is stored directly. For images with higher bit depth (16 and 32-bit) or for compressed images (2-bit), an 8-bit image is created for display (identical to the display in ODIS) and the original raw data is stored in a custom tag within the file.
B-Scan images are stored as multi-image TIFF files, and are subject to the limitations of the TIFF file size.
If the TIFF image is altered by an external program, it may no longer be readable by ODIS.
Binary Files as DICOM/DICONDE
A user may store the scan result data as a DICOM file (using the ASTM DICONDE specification for Ultrasonic Imaging). In this case, the binary file is a DICOM binary (.dcm) and can be read by a DICOM file reader.
both 8-bit and 16-bit data will be stored in the DICOM file. For images with a higher bit depth (32-bit), a 16-bit scaled image is saved.
B-Scan images are stored as multi-frame DICOM files.
If the DICOM image is altered by an external program, it may no longer be readable by ODIS.
Binary Information Files
The binary Information file describes the dimensions and units used to create the binary data. The filename of the binary Information file is identical to the binary data, with the exception of having a “.xml” as the extension. A typical Binary Information file is below.
<Scan>
<Info>
<name>Brd0:BScan1:WF</name>
<Xoffset>251</Xoffset>
<Yoffset>1315</Yoffset>
<Zoffset>0</Zoffset>
<Xscalemm>20</Xscalemm>
<Yscalemm>20</Yscalemm>
<Zscalemm>0</Zscalemm>
<Rotational>False</Rotational>
</Info>
<Size>
<Xsize>401</Xsize>
<Ysize>400</Ysize>
<WFsize>810</WFsize>
<SampleRate>500</SampleRate>
<ID>0</ID>
<OD>0</OD>
<MinMax>
<MinVal></MinVal>
<MaxVal></MaxVal>
</MinMax>
<Format>Raw</Format>
<Comments></Comments>
</Size>
</Scan>
- Scan
- the root element of the Binary information file
- Info
- this tag stores basic physical information about the scan.
- Name
- the scan name. This is a special format delineating the board, gate, feature, and row/column (in Tray scans) of the file. DO NOT EDIT MANUALLY.
- Xoffset
- the Scan offset (in image scan points) of the image from the 0 position in the tank.
- Yoffset
- the Step offset (in image scan lines) of the image from the 0 position in the tank.
- Zoffset
- the offset (in focus points) of the image from the 0 position in the tank. This is typically left at 0 unless the collection is a Beam Profile scan.
- Xscalemm
- the number of samples per unit on the Scan axis. Although this tag says "mm", in a system defined in inches, this value will be in samples/in.
- Yscalemm
- the number of scanlines per physical unit on the Step axis. Although this tag says "mm", in a system defined in inches, this value will be in scanlines/in.
- Zscalemm
- the number of points per physical unit on the focus axis. This is typically left at 0 unless the collection is a Beam Profile scan. Although this tag says "mm", in a system defined in inches, this value will be points/in.
- Rotational
- true if the scan was generated using a rotational axis (e.g. Turntable) for the scan axis.
- Size
- this tag stores information about the scan and step dimensions of the image
- Xsize
- the number of samples collected on the Scan Axis. Note that the size of a sample in bytes depends on the data type.
- Ysize
- the number of scan lines collected on the Step Axis.
- WFsize
- the length of the waveform collected, or the length of the waveform used to generate Frequency scans, in samples (if no waveform is collected, this is left at zero).
- SampleRate
- The sampling rate (in MHz) at the time the scan was collected.
- ID
- the Inner Diameter in physical units (if scanning with a turntable)
- OD
- the Outer diameter in physical units (if scanning with a turntable)
- MinVal
- the minimum digital value saved in this image. For 8-bit images, this would be -128. For TOF and similar images, this value will vary depending on the TOF settings.
- MaxVal
- the maximum digital value saved in this image. For 8-bit images, this would be 127. For TOF and similar images, this value will vary depending on the TOF settings.
- Format
- the format of the binary file. "Raw" or "TIFF". If missing, "Raw" is assumed.
- Comments
- user comment information about this particular feature.
Optional Files Details
Most of the other files you may encounter in a collection are not necessary to load and interpret the data. They are listed here for reference.
Palette Files (*.pal.xml)
Palette files contain an XML description of a series of boundaries and colors along an 8-bit palette. These are identical to the palette files used to set colors in ODIS.
See also: Palettes.
ScanAnnotation.xml Files
Annotation files contain an XML description of Annotations that can be displayed on an image in ODIS.
See also: Annotations.
ScanAnalysisSetup.analysis.xml and ScanAnalysisResults.xml Files
The ScanAnalysisSetup.analysis.xml file is the Analysis setup used to generate the Auto-Analysis results stored in ScanAnalysisResults.xml.
See Also: Auto-Analysis.
Info.xml Files
The Info.xml file contains user-entered info about the scan collection, such as the operator name, transducer type, and user notes.
AScan Files
AScan files contain waveform data collected at a specific point on the collection. If the collection was created with Waveform data, this data is identical to the waveform located at the same point.
B-Scan Start Times
For each B-Scan file, there will be another binary file with the extension ".start.bin" that has the same base name as the B-Scan, e.g. if the B-Scan filename is "Raw_Brd0_BScan_WF.bin", the start times filename will be called "Raw_Brd0_BScan_WF.start.bin". This file contains an array of integers that represent the absolute start time (in samples) of the first sample of the corresponding B-Scan waveform. For example, if the B-Scan data was collected at a 50 MHz sampling rate and the start time for a waveform is at 6.2 us, the start time will be stored as the integer value 310.
The start times are in the same order as in any C-Scan. It is not required to load the Start time data for the B-Scans unless the absolute start position of each waveform is needed for processing or display purposes.
Sub B-Scans and Patch Scans
In ODIS, users can specify regions to be rescanned. These generate Sub B-Scans or Patch Scan collections. Patch Scans and Sub B-Scans share much of the same information as the parent collection, and are stored in a sub-directory. Each directory is a complete Collection of its own, and can be loaded in the same way as the parent.
Procedure for Reading an ODIS Collection (Raw format)
To load a collection, the following steps should be performed (at minimum):
- Specify the directory in which to find the collection.
- Open the ScanCollection.xml file. If this is missing, exit.
- Find the Collection tag. If missing, exit.
- Find the Files tag. If missing, exit.
- For each file entry in the Files section:
- Determine the type of the file and the base file name. If unrecognized, exit
- using the base file name, load the Binary Information file
- Check for the Scan tag in the Binary information file. If missing, quit.
- Find the Size tag. If missing, exit.
- Read the XSize, YSize, and WFSize tags.
- Load the data based on the type of file:
- For Non-Waveform files:
- 8-bit data can be read with a byte buffer of size XSize * YSize
- 16-bit data can be read with a byte buffer of size XSize * YSize * 2
- 32-bit data can be read with a byte buffer of size XSize * YSize * 4
- 2-bit data can be read with a byte buffer of XSize * YSize / 4
- For Waveform files:
- A single page of 8-bit data can be read with a byte buffer of XSize * WFSize.
- The entire set of Waveform data can be read with a byte buffer of XSize * WFSize * YSize.
- A single page of 16-bit data can be read with a byte buffer of XSize * WFSize * 2.
- The entire set of Waveform data can be read with a byte buffer of XSize * WFSize * YSize *2.
- A single page of 8-bit data can be read with a byte buffer of XSize * WFSize.
- For Non-Waveform files:
- Load any optional information as required
- Load any Sub-Collections as required